ATP: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
==Scientific Background== | ==Scientific Background== | ||
[[File:ATP structure.png|thumb|Molecular structure of ATP]] | |||
ATP is a small but relatively complex organic molecule, consisting of an adenine nucleobase attached to the sugar ribose, which is in turn attached to a chain of three linked phosphate molecules. Breaking the link between the second and third phosphates in the chain via hydrolysis converts ATP to ADP (adenosine diphosphate), and results in the release of a free phosphate and a large amount of energy previously stored in the phosphate-phosphate bond. ADP can be further hydrolyzed to produce AMP (adenosine monophosphate) and release additional energy along with another phosphate. | ATP is a small but relatively complex organic molecule, consisting of an adenine nucleobase attached to the sugar ribose, which is in turn attached to a chain of three linked phosphate molecules. Breaking the link between the second and third phosphates in the chain via hydrolysis converts ATP to ADP (adenosine diphosphate), and results in the release of a free phosphate and a large amount of energy previously stored in the phosphate-phosphate bond. ADP can be further hydrolyzed to produce AMP (adenosine monophosphate) and release additional energy along with another phosphate. | ||
All living things on Earth rely on ATP for energy storage and transport, as well as | All living things on Earth rely on ATP for energy storage and transport, as well as using it for synthesizing RNA. It can also be converted into deoxyribose-adenosine triphosphate (dATP), which is used to make DNA. | ||
While ATP is ubiquitous in Earth life, it is entirely possible that alien life could use alternative energy-rich molecules instead of ATP, such as other nucleoside triphosphates (e.g. GTP, CTP, UTP), or more exotic molecules such as tetrazine or thiosulfate. | |||
Latest revision as of 23:04, 7 July 2025
Adenosine Triphosphate (commonly abbreviated as ATP and represented in-game by the symbol ![]() ) is a compound which serves as the primary "energy currency" of biological cells. It is generated primarily using Glucose
) is a compound which serves as the primary "energy currency" of biological cells. It is generated primarily using Glucose ![]() and is needed to keep your organism alive.
and is needed to keep your organism alive.
Scientific Background
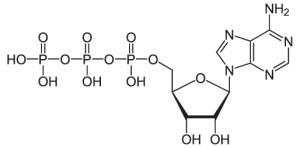
ATP is a small but relatively complex organic molecule, consisting of an adenine nucleobase attached to the sugar ribose, which is in turn attached to a chain of three linked phosphate molecules. Breaking the link between the second and third phosphates in the chain via hydrolysis converts ATP to ADP (adenosine diphosphate), and results in the release of a free phosphate and a large amount of energy previously stored in the phosphate-phosphate bond. ADP can be further hydrolyzed to produce AMP (adenosine monophosphate) and release additional energy along with another phosphate.
All living things on Earth rely on ATP for energy storage and transport, as well as using it for synthesizing RNA. It can also be converted into deoxyribose-adenosine triphosphate (dATP), which is used to make DNA.
While ATP is ubiquitous in Earth life, it is entirely possible that alien life could use alternative energy-rich molecules instead of ATP, such as other nucleoside triphosphates (e.g. GTP, CTP, UTP), or more exotic molecules such as tetrazine or thiosulfate.